Who is At Risk for Hepatitis C?
Who is At Risk for Hepatitis C?

Hepatitis C is a contagious liver disease caused by the Hepatitis C virus (HCV). It affects both adults and children, though some people may not show any symptoms. It can cause serious health complications, including cirrhosis or liver cancer if left untreated. Knowing who is at risk for contracting the virus is vital in preventing it from spreading further.
In this article, we’ll discuss who is most at risk for Hepatitis C, what screening options are available, and how to prevent hepatitis.
How is Hep C Spread?
One of the most common ways Hep C is spread is through contact with blood from an infected person. This includes sharing needles, syringes, or other drug equipment. Although rare, sexual transmission is also possible, as well as being born to a mother who has Hepatitis C. It can also be spread by coming into contact with contaminated objects such as razors or toothbrushes. Additionally, receiving tattoos in unsterile environments may increase the risk of contracting hepatitis C if there was blood present that was previously exposed to HCV-infected blood.
While it’s possible for Hepatitis C to be transmitted through saliva and other bodily fluids, this type of transmission is one of the less common ways Hep C is spread—as long as there are no open sores or cuts in the skin that could allow infected fluid to enter the body. Healthcare workers are at a higher risk of exposure than most people, due to their frequent contact with patients’ blood and bodily fluids while on duty. However, proper safety protocols including sterile gloves should reduce any potential risks significantly.
It is important for anyone who may have been exposed to the virus—even if they do not currently show symptoms—to get tested and seek treatment right away before any complications arise. This will prevent the infection from spreading further in their bodies.
Can You Be Asymptomatic and Spread Hepatitis C?
It’s possible to be infected with the Hepatitis C virus and be asymptomatic—meaning you have no symptoms of the infection. Most people who are infected with HCV do not experience any symptoms for several months or even years after being exposed to the virus. That means that many individuals may unknowingly spread the virus without realizing they have it due to a lack of noticeable signs and symptoms.
Being asymptomatic does not mean that an individual cannot transmit hepatitis C through contact with their bodily fluid. Those who are unaware they have contracted HCV could potentially spread it more easily than someone who has been diagnosed and is taking steps to prevent transmission. Therefore, it is important to understand how Hepatitis C can be passed between people even if neither person experiences any visible signs or symptoms of the disease.
How Soon Will Hep C Show Up After Exposure?
Knowing how soon HCV will show up after exposure to the virus is important for those at risk. They must seek treatment right away before any complications arise from the infection spreading further in their bodies.

Who is Most at Risk for Hepatitis C?
People who use injection drugs are particularly vulnerable to the Hepatitis C virus due to their increased likelihood of sharing needles, which can spread the virus if they come into contact with infected blood. People who received a blood transfusion before 1992 may also be at high risk, as safety protocols were not yet available that could adequately screen out potentially contaminated donations during this period.
In addition to those considered “high risk” for hepatitis C infection, there are several other parties who fall under moderate levels of potential exposure. These include people born between 1945 and 1965 (the “baby boomer” generation), current or former prison inmates, HIV-positive individuals, and hemodialysis patients, among others.
Can You Get Hep C More Than Once?
Yes, it’s possible to contract Hepatitis C (HCV) more than once. While the virus typically remains in an infected person’s body for life, recurrence of HCV infection is not unheard of.
Transmission of hepatitis can occur more than once if a person encounters the virus again and has weakened immunity due to other conditions. If their immune system does not recognize it or cannot fight off the new strain, they may be re-infected. Additionally, individuals who have undergone organ transplants may also encounter this issue, since there is potential for exposure through donor tissues containing traces of Hepatitis C.
How to Prevent Hepatitis C
One of the most important steps to prevent Hepatitis C (HCV) is to be aware of the potential risks associated with contracting this virus and take action to protect oneself from exposure. Those at high risk for Hepatitis C infection must take extra precautions when engaging in activities outside their home which may place them at greater risk of coming into contact with contaminated objects or fellow individuals carrying the virus. This includes avoiding sharing needles/syringes used for injection drugs, having protected sexual activity, and only receiving tattoos from reputable tattoo shops.
Additionally, those living in close quarters, such as military personnel, inmates, and students attending college dormitories should also maintain personal hygiene regularly. This includes washing hands frequently and using disposable paper towels instead of cloths.
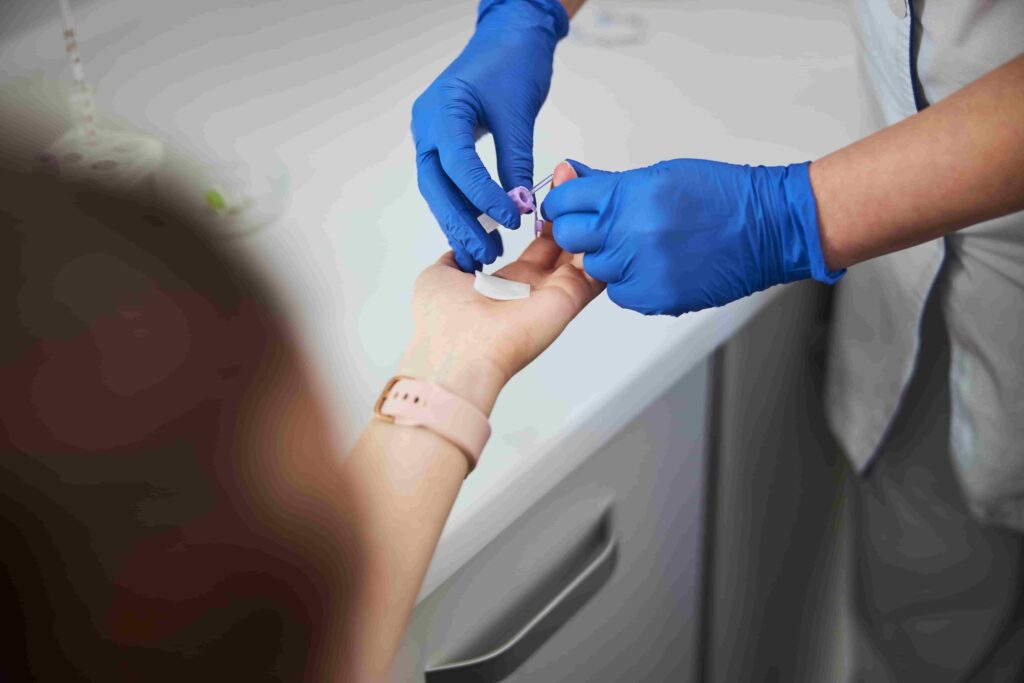
Ultimately knowing one’s status will better equip an individual to prevent Hepatitis C from becoming severe.
Learn More About Hepatitis C Screening
Hepatitis C Testing with CATC
Are you concerned that you or someone you know may have contracted Hep C? For those who may be unsure if they have been exposed to Hepatitis C, it’s important to contact us at Canadian Addiction Treatment Centres (CATC) to get screened. Through our screening services at CATC, individuals at risk of contracting Hepatitis C can take proactive steps toward staying safe before symptoms appear or become more severe. For anyone who has been diagnosed, we also have a comprehensive Hepatitis C treatment program which can help you get your health back.